Thursday, October 31, 2013
Tuesday, October 22, 2013
Wednesday, October 9, 2013
WW 5 - Learning Strategy
This week the lesson on topic learning strategy. The Learning Strategy is the way we approach to determine and achieve the learning objective.
There are few learning strategies that are well known :
There are few learning strategies that are well known :
- Problem Solving - a student- centered pedagogy where the student try to solve by using methodical approach.
- Problem Based Learning - a student-centered pedagogy in which students learn about a subject through the experience of problem solving. Students learn both thinking strategies and domain knowledge
- Collaborative Learning - learning based on peer or group.
- Inquiry Based Learning - a student-centered and teacher-guided instructional approach that engages students in investigating real world questions
There are to important terms to describe our thesis or research, there were:
- Validity - it is a approval that we receive from the expert. Expert of content and design
- Reliability - it is a questionnaire that we tested on small group before the real target. It must have pretest and post test.
Wednesday, October 2, 2013
WW3 - Web Development Process
This topic is quite interesting. We need a system/method to follows before create a web. in education, create a website is no meaning if the content cannot attract the user or improve the user or achieve the objective of the website.
Instructional Design (ID) Model
Instructional Design is the systematic development of instructional specifications using learning and instructional theory to ensure the quality of instruction. It is the entire process of analysis of learning needs and goals and the development of a delivery system to meet those needs.
Analysis
During analysis, the designer identifies the learning problem, the goals and objectives, the audience’s needs, existing knowledge, and any other relevant characteristics. Analysis also considers the learning environment, any constraints, the delivery options, and the timeline for the project.
Design
A systematic process of specifying learning objectives. Detailed storyboards and prototypes are often made, and the look and feel, graphic design, user-interface and content is determined here.
Development
The actual creation (production) of the content and learning materials based on the Design phase.
Implementation
During implementation, the plan is put into action and a procedure for training the learner and teacher is developed. Materials are delivered or distributed to the student group. After delivery, the effectiveness of the training materials is evaluated.
Evaluation
This phase consists of (1) formative and (2) summative evaluation. Formative evaluation is present in each stage of the ADDIE process. Summative evaluation consists of tests designed for criterion-related referenced items and providing opportunities for feedback from the users. Revisions are made as necessary.
Instructional Design (ID) Model
Instructional Design is the systematic development of instructional specifications using learning and instructional theory to ensure the quality of instruction. It is the entire process of analysis of learning needs and goals and the development of a delivery system to meet those needs.
ADDIE Model
The five phases of ADDIE are as follows:
Analysis
During analysis, the designer identifies the learning problem, the goals and objectives, the audience’s needs, existing knowledge, and any other relevant characteristics. Analysis also considers the learning environment, any constraints, the delivery options, and the timeline for the project.
Design
A systematic process of specifying learning objectives. Detailed storyboards and prototypes are often made, and the look and feel, graphic design, user-interface and content is determined here.
Development
The actual creation (production) of the content and learning materials based on the Design phase.
Implementation
During implementation, the plan is put into action and a procedure for training the learner and teacher is developed. Materials are delivered or distributed to the student group. After delivery, the effectiveness of the training materials is evaluated.
Evaluation
This phase consists of (1) formative and (2) summative evaluation. Formative evaluation is present in each stage of the ADDIE process. Summative evaluation consists of tests designed for criterion-related referenced items and providing opportunities for feedback from the users. Revisions are made as necessary.
Source: Here
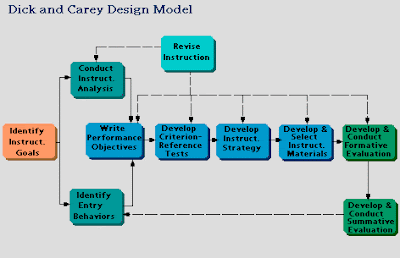
Dick and Carey Model
Stage 1. Instructional Goals
Stage 1. Instructional Goals
* Instructional Goal: Desirable state of affairs by instruction
* Needs Analysis : Analysis of a discrepancy between an instructional goal and the present state of affairs or a personal perception of needs.
Stage 2. Instructional Analysis
* Needs Analysis : Analysis of a discrepancy between an instructional goal and the present state of affairs or a personal perception of needs.
Stage 2. Instructional Analysis
* Purpose : To determine the skills involved in reaching a goal
* Task Analysis (procedural analysis) : about the product of which would be a list of steps and the skills used at each step in the procedure
* Information-Processing Analysis : about the mental operations used by a person who has learned a complex skills
* Learning-Task Analysis : about the objectives of instruction that involve intellectual skills
Stage 3. Entry Behaviors and Learner Characteristics* Purpose : To determine which of the required enabling skills the learners bring to the learning task
* Intellectual skills
* Abilities such as verbal comprehension and spatial orientation
* Traits of personality
Stage 4. Performance Objectives
* Task Analysis (procedural analysis) : about the product of which would be a list of steps and the skills used at each step in the procedure
* Information-Processing Analysis : about the mental operations used by a person who has learned a complex skills
* Learning-Task Analysis : about the objectives of instruction that involve intellectual skills
Stage 3. Entry Behaviors and Learner Characteristics* Purpose : To determine which of the required enabling skills the learners bring to the learning task
* Intellectual skills
* Abilities such as verbal comprehension and spatial orientation
* Traits of personality
Stage 4. Performance Objectives
* Purpose : To translate the needs and goals into specific and detailed objectives
* Functions : Determining whether the instruction related to its goals.
Focusing the lesson planning upon appropriate conditions of learning
Guiding the development of measures of learner performance
Assisting learners in their study efforts.
Stage 5. Criterion-Referenced Test Items
* Functions : Determining whether the instruction related to its goals.
Focusing the lesson planning upon appropriate conditions of learning
Guiding the development of measures of learner performance
Assisting learners in their study efforts.
Stage 5. Criterion-Referenced Test Items
*To diagnose an individual possessions of the necessary prerequisites for learning new skills
*To check the results of student learning during the process of a lesson
*To provide document of students progress for parents or administrators
*Useful in evaluating the instructional system itself (Formative/ Summative evaluation)
*Early determination of performance measures before development of lesson plan and instructional materials
Stage 6. Instructional Strategy
*To check the results of student learning during the process of a lesson
*To provide document of students progress for parents or administrators
*Useful in evaluating the instructional system itself (Formative/ Summative evaluation)
*Early determination of performance measures before development of lesson plan and instructional materials
Stage 6. Instructional Strategy
* Purpose : To outline how instructional activities will relate to the accomplishment of the objectives
*The best lesson design : Demonstrating knowledge about the learners, tasks reflected in the objectives, and effectiveness of teaching strategiese.g. Choice of delivering system.
Teacher-led, Group-paced vs. Learner-centered, Learner-paced
Stage 7. Instructional Meterials
*The best lesson design : Demonstrating knowledge about the learners, tasks reflected in the objectives, and effectiveness of teaching strategiese.g. Choice of delivering system.
Teacher-led, Group-paced vs. Learner-centered, Learner-paced
Stage 7. Instructional Meterials
* Purpose : To select printed or other media intended to convey events of instruction.
* Use of existing materials when it is possible
* Need for development of new materials, otherwise
* Role of teacher : It depends on the choice of delivery system
Stage 8. Formative Evaluation
* Use of existing materials when it is possible
* Need for development of new materials, otherwise
* Role of teacher : It depends on the choice of delivery system
Stage 8. Formative Evaluation
* Purpose : To provide data for revising and improving instructional materials
* To revise the instruction so as to make it as effective as possible for larger number of students
* One on One : One evaluator sitting with one learner to interview
* Small Group
* Field Trial
Stage 9. Summative Evaluation
* To revise the instruction so as to make it as effective as possible for larger number of students
* One on One : One evaluator sitting with one learner to interview
* Small Group
* Field Trial
Stage 9. Summative Evaluation
* Purpose : To study the effectiveness of system as a whole
* Conducted after the system has passed through its formative stage
* Small scale/ Large Scale
* Short period/ Long period
* Conducted after the system has passed through its formative stage
* Small scale/ Large Scale
* Short period/ Long period
Source : Here
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)